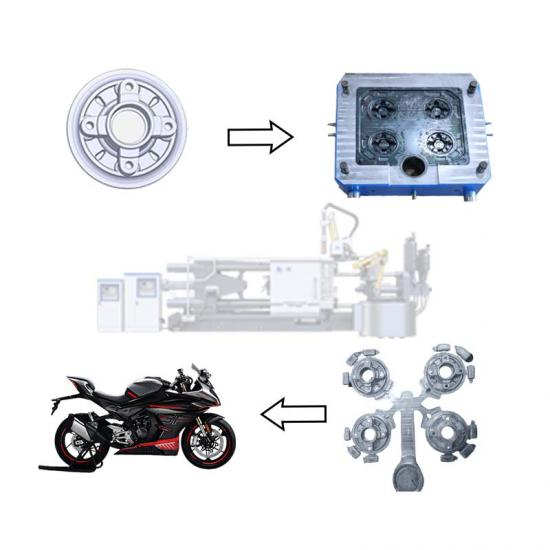
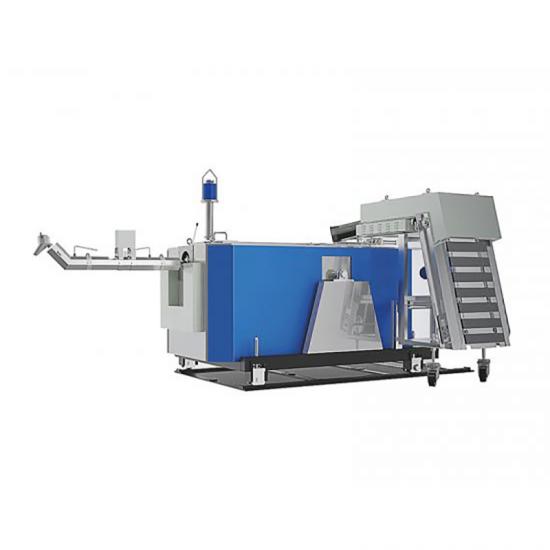
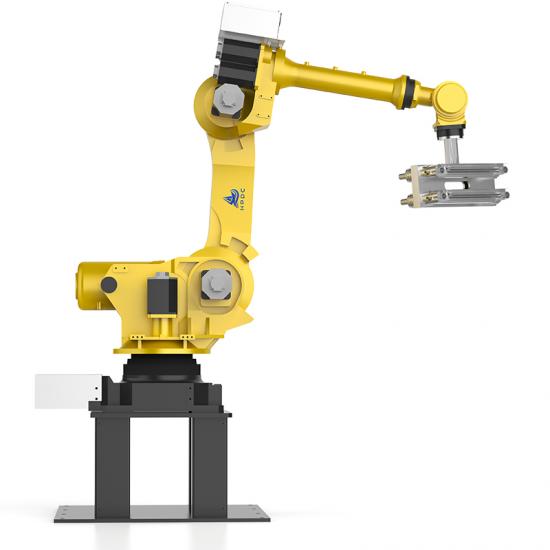
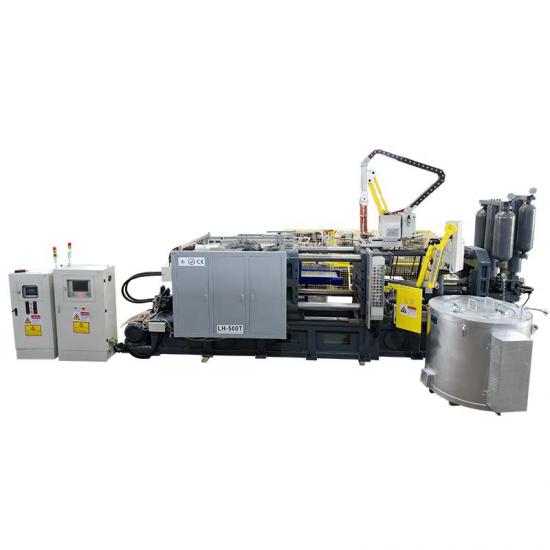
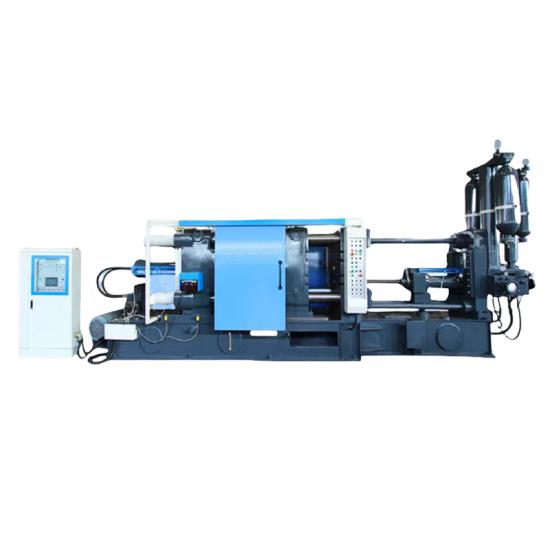
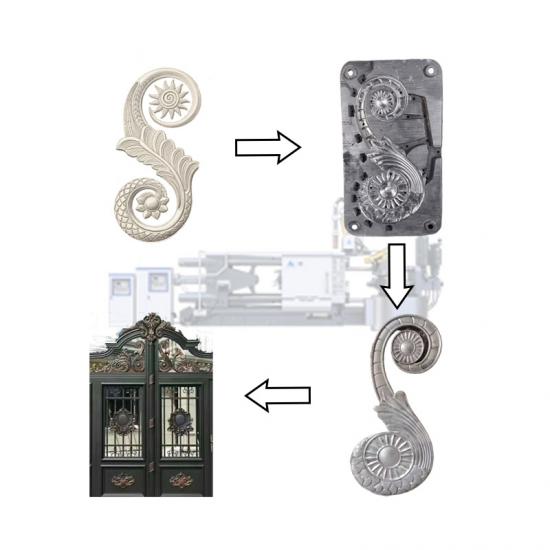
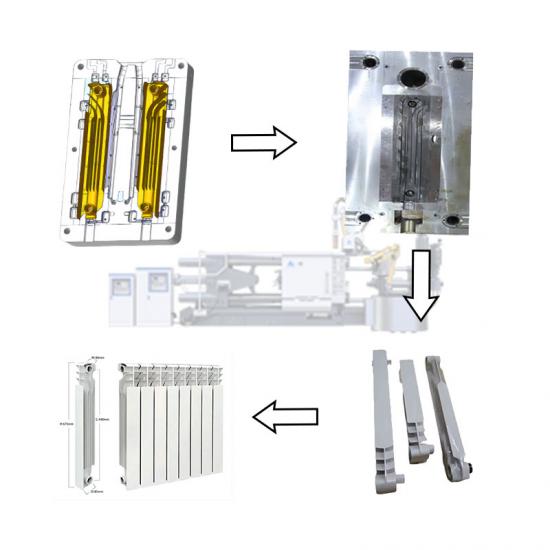
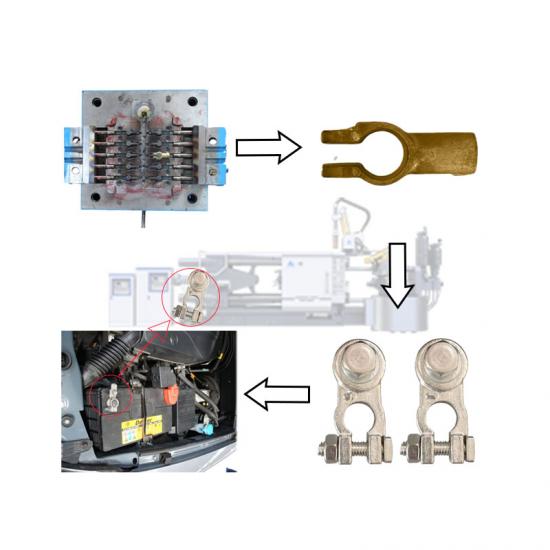
Pressure casting (referred to as die casting) is to fill the die casting cavity (die casting mold) with liquid or semi-solid metal at a high speed under high pressure, and to form and solidify under pressure to obtain castings. Die castings have high dimensional accuracy, generally equivalent to level 6~7, or even level 4; low surface roughness; high strength and hardness, 25%~30% higher than sand casting, stable dimensions, good interchangeability; thin-walled complex castings can be die-cast, with high production efficiency and long die-casting mold life. When die-casting aluminum alloys, it can reach 80,000~200,000 times, so the die-casting process is widely used in photovoltaics, 5G communications and automotive fields.
Aluminum and aluminum alloys have low density (close to 2.7g/cm³), which is about 1/3 of iron or copper; good electrical and thermal conductivity, second only to silver, copper and gold; good corrosion resistance: the surface of aluminum is easy to naturally produce a dense and firm Al2O3 protective film, which can well protect the substrate from corrosion. Good products can be obtained through passivation, powder spraying, coating, etc., so it is particularly suitable for die-casting production.
The composition of various standard aluminum alloy materials is similar, and alloy materials can be selected according to the use requirements. Conventional die-cast aluminum alloys have no special requirements for elongation and thermal conductivity, and are mainly used for automobile and motorcycle engine parts, such as engine covers, oil pans, cylinder blocks, transmission housings, etc.
With the development of 5G technology, more and more die-cast aluminum alloys are used in communication base stations, mainly for the production of radiator housings. Since the thermal conductivity of traditional ADC12 aluminum alloy is only 100W/(m·K), ENAC44300 is generally selected as the die-casting material to improve the thermal conductivity of the parts; in addition, T5 heat treatment at 200~350℃ can be used. In addition to the 5G communication field, the photovoltaic industry also has an increasing demand for die-cast aluminum alloys, and the representative component is the inverter housing. "Photovoltaic + energy storage" has become the standard configuration for photovoltaic development in many countries. After matching energy storage, it will bring long-term and sustainable development momentum to photovoltaics. It is estimated that the global photovoltaic installed capacity will increase by 370GW in 2025, and the new demand for energy storage inverters will be about 74GW by then. Experts predict that by 2025, 2% of the world's energy supply will come from photovoltaic power generation. By 2055, photovoltaic power generation will deliver more energy, accounting for about 25% of the total energy supply, and will exceed 50% by 2150. In addition to the need for thermal conductivity, this type of aluminum alloy also has certain requirements for elongation in order to deal with accidental explosions without generating fragments, usually requiring more than 5%. The main components in the heat dissipation field mainly include ADS housings, DC converters, base station radiators, photovoltaic inverters, chargers, vehicle radiators, and headlight radiators.
Whether it is a new high thermal conductivity aluminum alloy or a heat-treatment-free die-cast aluminum alloy, improving thermal conductivity and elongation requires reducing the content of alloy elements and keeping the types of alloy elements as small as possible to meet performance requirements. In addition to meeting product performance requirements, die-casting aluminum alloys should also have the following properties to ensure die-casting process and product appearance quality: ① Good thermoplasticity near the solidus temperature to achieve complex cavity filling and avoid shrinkage; ② Low shrinkage to avoid cracks and deformation during die-casting and improve dimensional accuracy; ③ Smaller solidification interval (temperature difference between liquidus and solidus) to reduce shrinkage; ④ Good high-temperature strength to avoid cracking during mold opening; ⑤ Good casting/mold interface performance to avoid reaction with the mold and alleviate mold sticking; ⑥ Good physical and chemical properties, not easy to absorb air and oxidize in the high-temperature molten state, meeting the long-term insulation requirements.
The development trend of die-casting products is towards integration and large-scale development; with the development of product characteristics and the demand for personalized performance, die-casting aluminum alloys are developing towards low alloying; high vacuum die-casting has become an important means to solve the process problems of new die-casting aluminum alloy materials.