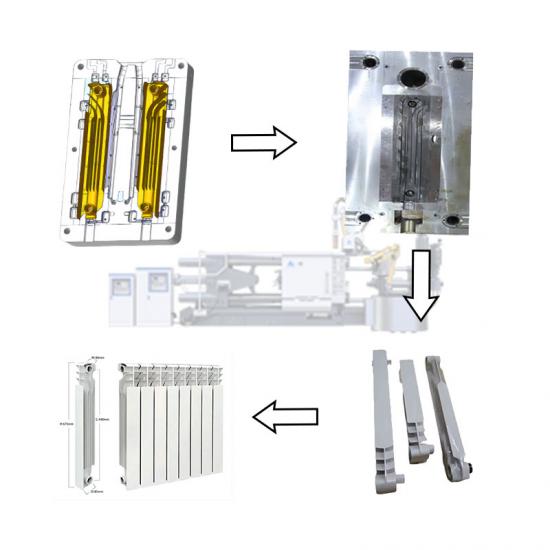
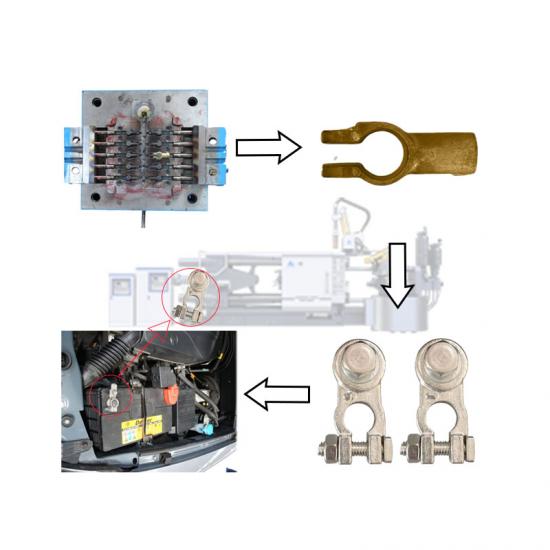
There are many types of casting defects, and the causes of defects are also very complicated. Therefore, when analyzing the causes of casting defects, we should start from the specific situation, conduct a comprehensive analysis based on the characteristics, location, process and sand used, and then take corresponding technical measures to prevent and eliminate defects.
1. Not pouring
Prevention methods:
Increase the pouring temperature, speed up the pouring speed, and prevent intermittent pouring;
Increase the cross-sectional area of the runner and the inner runner;
Adjust the post-furnace batching to appropriately increase the carbon and silicon content;
Strengthen the exhaust in the casting mold, reduce the amount of coal powder and organic matter added in the sand;
Increase the height of the upper sand box.
2. Not full
Prevention methods:
Correctly estimate the amount of molten iron in the ladle;
For castings with narrow runners, appropriately slow down the pouring speed to ensure that the casting is full.
3. Damage
Prevention methods:
When cleaning and transporting castings, pay attention to avoid various forms of excessive collision and vibration, and avoid unreasonable dropping;
When cleaning the drum, strictly follow the process regulations and requirements;
Modify the size of the riser and the riser neck, make the riser neck knock section, and correctly grasp the direction of the pouring riser.
4. Sticky sand and rough surface
Prevention methods:
When the air permeability is sufficient, use finer raw sand and appropriately increase the compactness of the molding sand;
Ensure a stable effective coal powder content in the molding sand;
Strictly control the moisture content of the sand;
Improve the pouring system, improve the pouring operation, and reduce the pouring temperature;
Control the template baking temperature, which is generally equal to or slightly higher than the molding sand temperature.
5. Sand holes
Prevention methods:
Increase the sticky sand content in the molding sand, add new sand in time, and improve the surface strength of the molding sand;
The mold finish should be high, and the draft angle and casting fillet should be reasonably made. Damaged molds should be repaired before assembling;
Shorten the placement time of sand molds before pouring;
Be careful when assembling or transporting molds to avoid damage or sand particles falling into the sand mold cavity;
Remove floating sand in the mold before assembling and cover the gate.
6. Seam filling and sand expansion
Prevention methods:
Improve the compactness of the mold and avoid local looseness;
Adjust the sand mixing process, control the water content, and improve the strength of the mold sand;
Reduce the pressure head of the liquid metal and reduce the pouring speed.
7. Lifting the box
Prevention methods: Increase the weight of the iron weight, and remove the iron weight after the molten iron solidifies;
Lower the position of the ladle and reduce the pouring speed;
Correct the template.
8. Sand drop
Prevention methods:
The draft angle of the mold should be appropriate and the surface should be smooth;
The compactness of the mold should be high and uniform;
Be careful during assembling and transportation.
9. Mismatch (mismatched box)
Prevention methods:
Strengthen the inspection and repair of the template;
Frequently check the positioning pins and pin holes of the sand box and template, and install them reasonably;
Check the relevant parts of the extrusion molding machine, adjust them in time, and replace those with severe wear;
Regularly reshape the box. Be careful when carrying the casting after removing the box. For the sand mold poured on the surface, a row of sand molds should be surrounded by a row.
10. Gray mouth and pitting
Prevention methods:
Correctly select the chemical composition and reasonably mix the ingredients to make the carbon and silicon content in the molten iron within the specified range;
Increase the amount of bismuth added and strictly follow the furnace inoculation process.
11. Cracks (hot cracks, cold cracks)
Prevention methods:
Control the chemical composition of the molten iron within the specified range;
Lower the pouring temperature;
Reasonably design the riser system;
Avoid excessive impact during cleaning and transportation of castings.
12. Porosity
Prevention methods:
Furnace charge should be properly managed and the surface should be clean;
Furnace hearth, forehearth, tap hole, tap trough and ladle must be dried;
Increase pouring temperature;
Do not use scrap steel with too high aluminum content;
Appropriately reduce the moisture content of molding sand, control the amount of coal powder added, pierce the air holes, etc.
13. Shrinkage and looseness
Prevention methods:
Control the chemical composition of molten iron within the specified range;
Reduce the pouring speed and pouring temperature;
Improve the pouring and riser system and use sequential solidification;
Increase the riser volume to ensure sufficient shrinkage compensation.
14. Chilling
Prevention methods:
Control the chemical composition, carbon and silicon content should not be too high;
Furnace lining and ladle lining should be dried; The moisture content of molding sand should not be too high;
Strengthen charge management to reduce the introduction of chilling elements.