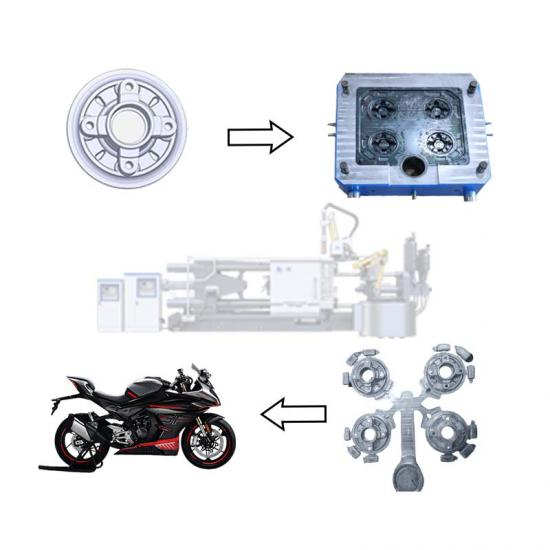
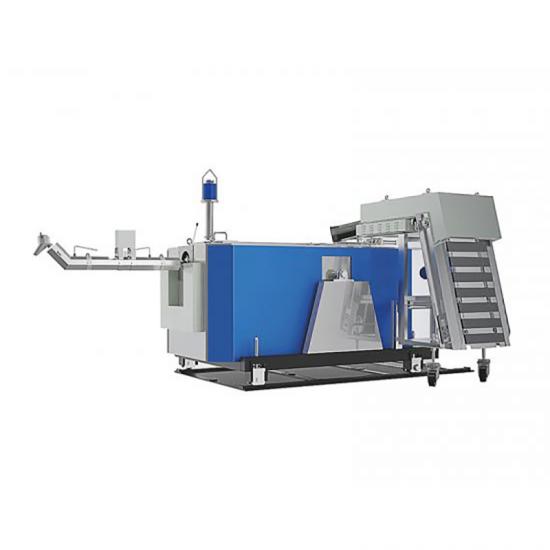
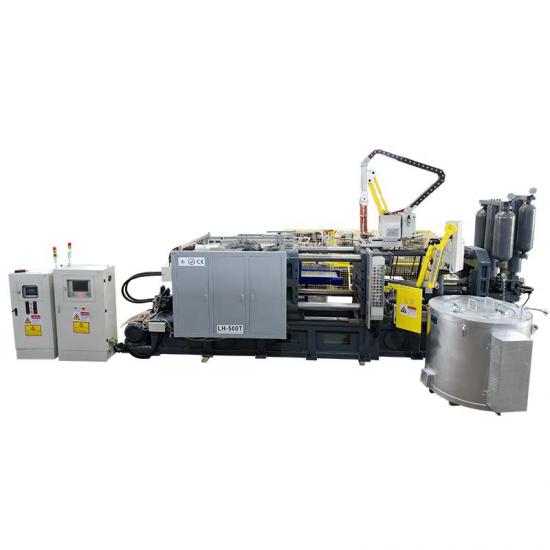
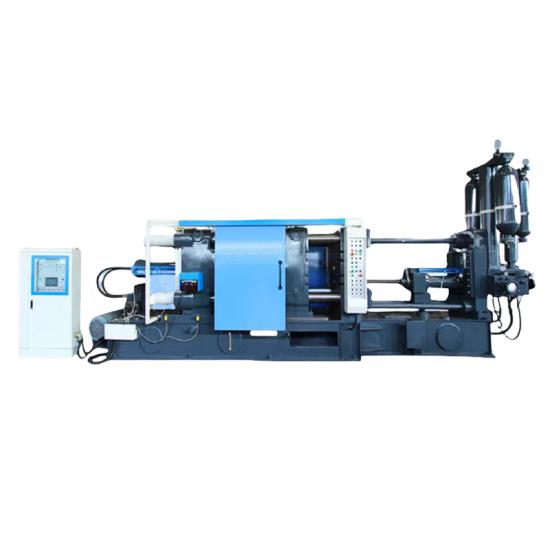
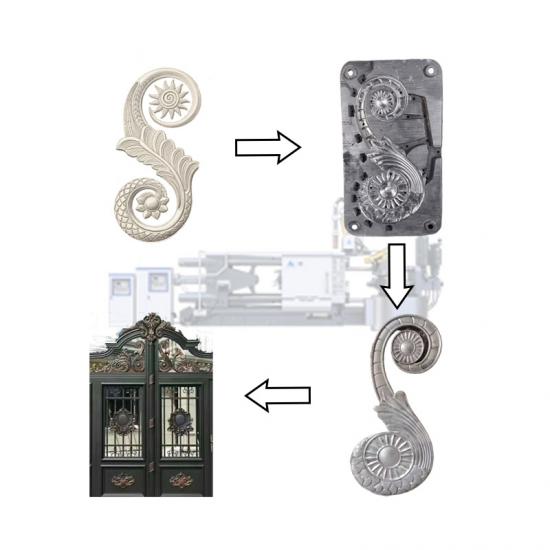
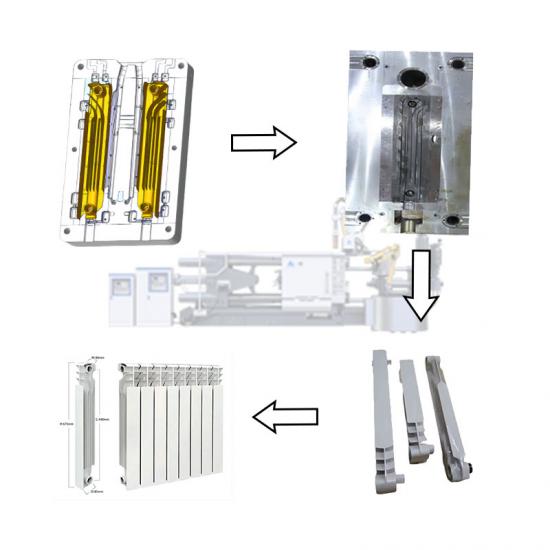
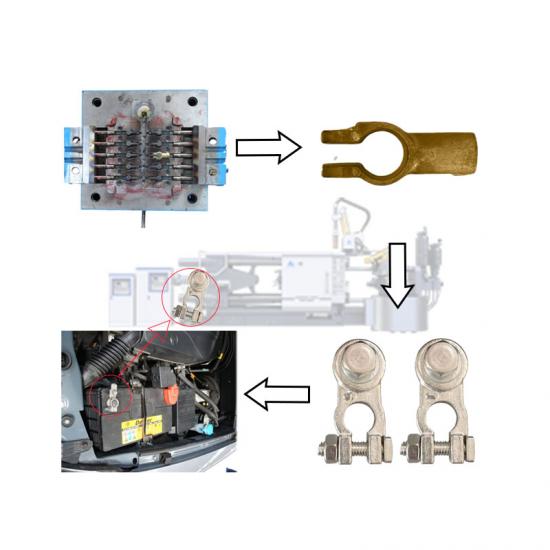
In the die - casting process, hot - chamber and cold - chamber die - casting machines are two common types of equipment. They may seem similar, but actually have significant differences in many aspects.
In terms of structure, the injection system of the hot - chamber die - casting machine is directly immersed in the molten metal of the furnace. It scoops and injects the metal through a gooseneck tube, featuring a compact structure and a simple operation process. On the other hand, the injection chamber of the cold - chamber die - casting machine is separated from the furnace. During die - casting, the molten metal needs to be ladled into the injection chamber first and then injected, resulting in a relatively complex structure.
Regarding the working principle, the hot - chamber die - casting machine uses air pressure to push the piston, forcing the molten metal into the mold cavity through the gooseneck tube. It has a high production efficiency and is suitable for producing small, thin - walled castings made of zinc alloys, lead alloys, etc. The cold - chamber die - casting machine uses hydraulic pressure to drive the injection punch, injecting the molten metal in the injection chamber into the mold at high speed. It is suitable for manufacturing large, thick - walled castings made of aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys.
In terms of production efficiency, the hot - chamber die - casting machine has a short operation process and can quickly complete the die - casting cycle, thus achieving high production efficiency. For the cold - chamber die - casting machine, since the molten metal needs to be ladled and then injected, the preparation time is longer, leading to relatively lower production efficiency.
In terms of cost, the hot - chamber die - casting machine has a simple structure and a low equipment cost. However, due to its long - term exposure to high - temperature molten metal, key components are prone to damage, resulting in high maintenance costs. The cold - chamber die - casting machine has a high equipment cost, but the maintenance cost is low during normal operation.Understanding these differences helps enterprises rationally select die - casting equipment according to their own needs and production goals, thereby improving production efficiency and benefits.