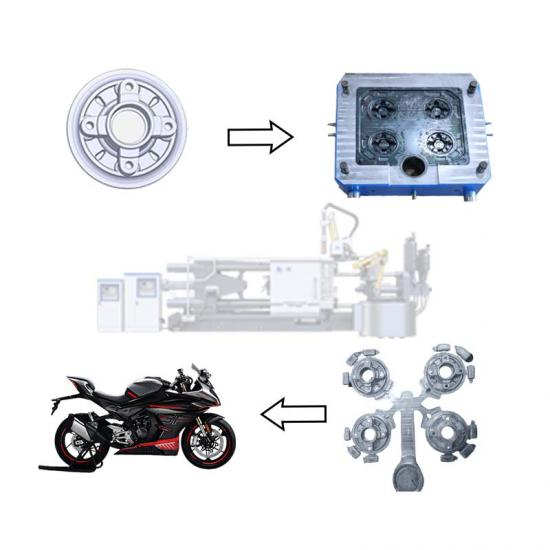
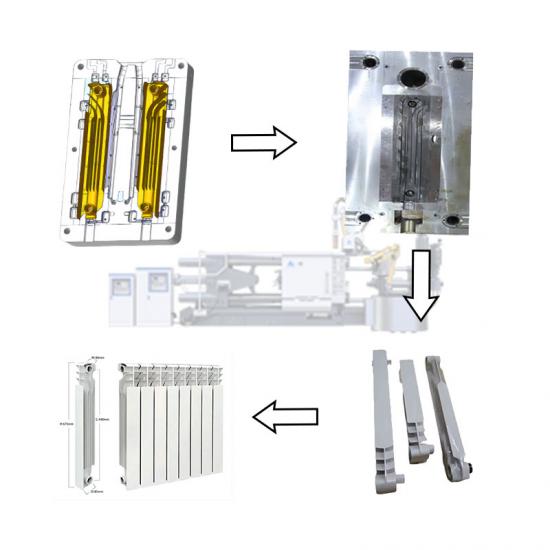
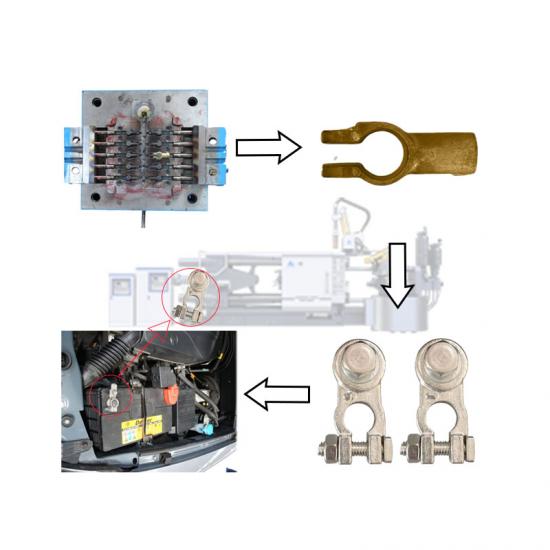
The die casting process of brake pads involves a series of steps to ensure that high-quality products are manufactured to meet automotive safety standards. The following is a typical brake pad die casting process:
1. Material preparation
The materials of brake pads usually include friction materials, adhesives and metal backing plates. The preparation of die casting materials includes selecting the appropriate friction material formula and metal.
2. Mold preparation
According to the design requirements of the brake pad, a special die casting mold is made. The mold is usually made of high-temperature resistant and high-strength steel to ensure service life and die casting quality.
3. Heating
Preheat the metal backing plate and mold to the appropriate temperature to ensure that the materials can be evenly distributed and form a good bond during the die casting process.
4. Die casting
Metal backing plate placement: Place the preheated metal backing plate into the mold.
Friction material injection: The friction material is injected into the mold at high pressure so that it evenly fills the mold and covers the metal backing plate.
Pressure molding: High pressure is applied by the press to firmly bond the friction material to the metal backing plate and form the predetermined brake pad shape.
5. Cooling and curing
The mold is allowed to cool so that the friction material solidifies and reaches the necessary mechanical properties. The cooling time and conditions vary depending on the material and mold design.
6. Demolding
The molded brake pad is removed from the mold and inspected for defects such as pores, cracks, etc.
7. Post-processing
The demolded brake pad is subjected to necessary post-processing, including deburring, cleaning, heat treatment and other steps to improve its durability and performance.
8. Inspection and testing
The brake pad is subjected to rigorous quality inspection and performance testing to ensure that it meets relevant standards and customer requirements. Common test items include hardness testing, wear resistance testing, shear strength testing, etc.
9. Packaging and shipping
Qualified brake pads are packaged, clearly marked, and ready to be shipped to customers or assembly plants.
Through the above steps, manufacturers are able to produce brake pads that meet safety and performance standards to ensure vehicle braking performance and driving safety.