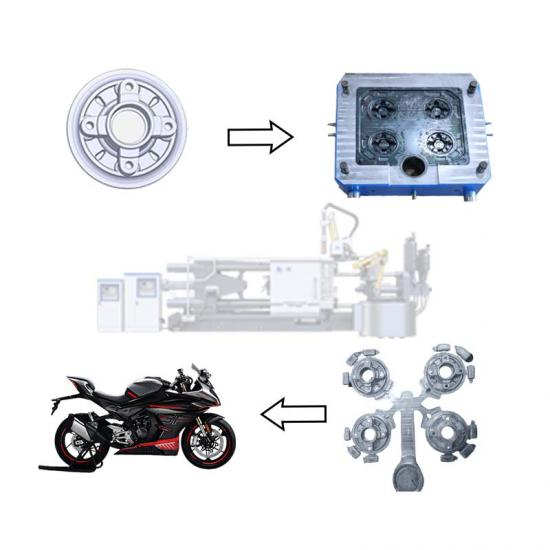
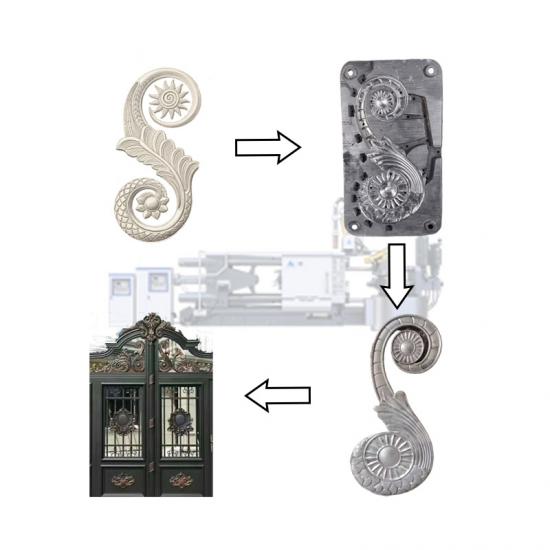
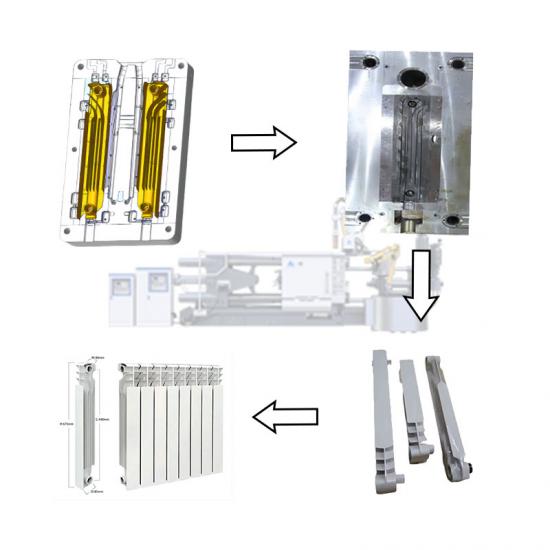
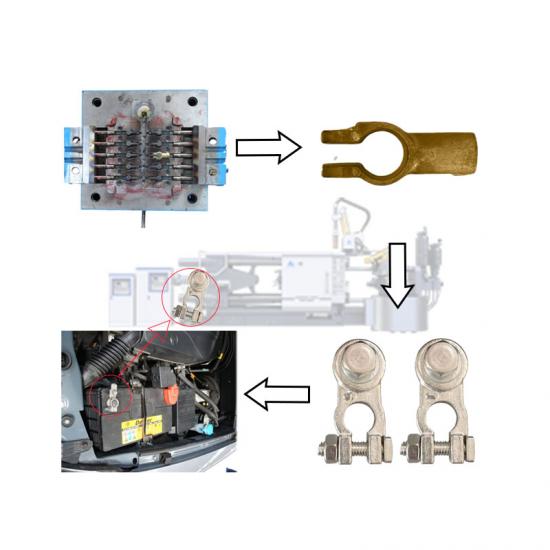
The die casting process of cookware involves forming metal (usually aluminum alloy) into a specific shape through a mold. This process ensures that the cookware has excellent thermal conductivity, durability and beautiful appearance. The following is the detailed process of cookware die casting:
1. Material preparation
Metal raw materials: Aluminum alloy is usually selected because of its light weight and good thermal conductivity.
Alloy smelting: The aluminum alloy is melted in a furnace and appropriate alloying elements are added to improve the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the material.
2. Mold design and production
Mold design: The mold is designed according to the shape and size of the cookware. The mold needs to have high precision and high temperature resistance.
Mold production: The mold is made of high-strength steel and finely processed to ensure that the mold surface is smooth and meets the design requirements.
3. Mold preheating
Before die casting, the mold is preheated. Preheating helps the metal to be more evenly distributed when injected into the mold, reducing pores and cold shut defects.
4. Die casting
Metal injection: The molten aluminum alloy is injected into the preheated mold through the die casting machine. High pressure causes the metal to quickly fill the mold and form the basic shape of the pot.
Cooling and solidification: Maintain high pressure and wait for the aluminum alloy to cool and solidify, usually a few seconds to a few minutes.
5. Demolding
Once the metal cools and solidifies, open the mold and carefully remove the formed pot blank.
6. Post-processing
Trimming and deburring: Remove excess material and burrs generated during the die-casting process to make the edges smooth.
Machining: Further processing such as drilling, turning and milling is performed as needed to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
7. Surface treatment
Polishing and grinding: Polish and grind the surface of the pot to enhance its gloss and beauty.
Spraying or electroplating: Spraying or electroplating treatment is performed according to product requirements to increase the appearance effect and improve corrosion resistance.
Non-stick coating: Many pots need to be coated with non-stick coating to ensure that food does not stick to the pot during cooking.
8. Quality inspection
Strict quality inspection of the finished product to ensure that it meets the design specifications and quality standards. Inspection items include appearance inspection, dimensional measurement, coating adhesion test, etc.
9. Packaging and Shipping
Qualified cookware is packaged to prevent damage during transportation and is ready to be shipped to customers or retailers.
Through the above steps, manufacturers can produce high-quality cookware to meet market demand and ensure that consumers have a good experience during use.